SkillsPlanner’s planned use of linked and open data to collate construction skills supply and demand data fits with wider ambitions to make data a driver for economic growth and prosperity.
According to a recent RICS survey reported in the construction trade press (see this Construction Enquirer article, for example), skills shortages are hampering construction projects across the UK. With subcontractors facing rising wage bills, it is becoming more difficult for them to accurately forecast project costs, causing delays to project planning.
And this is not just a short-term problem. Significant skills gaps lasting into the next decade have been identified by research including the London Chamber of Commerce & Industry/KPMG 2014 report ‘Skills to Build’ (PDF here) and the September 2015 National Infrastructure Plan for Skills (PDF here). It is timely, therefore, that the Ethos-led and Innovate UK-funded SkillsPlanner research and development project is now well under way.
What is SkillsPlanner?
SkillsPlanner is an innovative, collaborative, data-powered approach to addressing construction industry skills shortages. Its ambition is to help ensure that the UK has the right people, with the right skills, in the right places, at the right time.
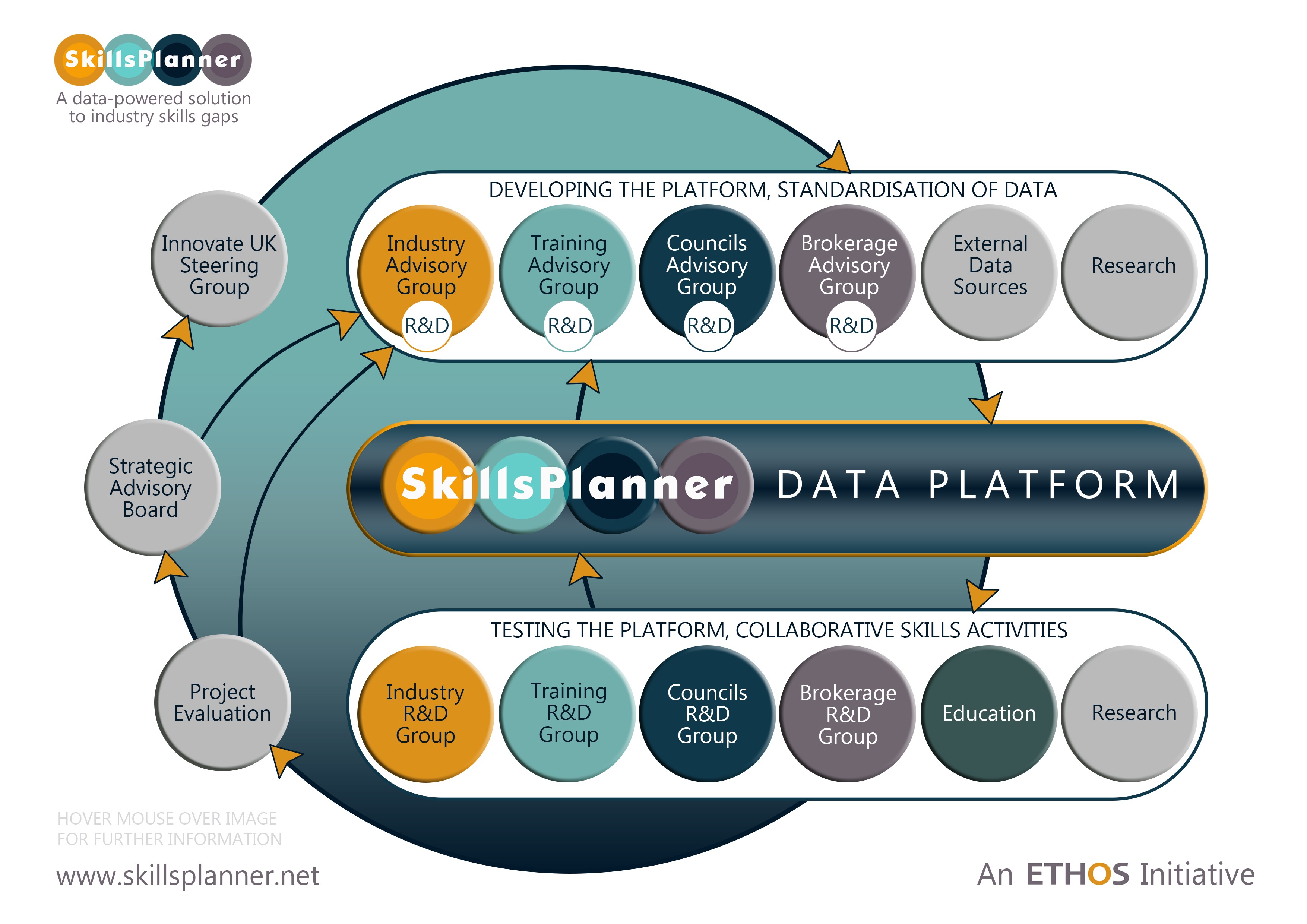
The two-year, £1.3m research and development programme, funded by Innovate UK and the project partners – Ethos, GoodPeople, Association of Colleges, Camden, Islington and Westminster councils, Seme4, Tideway, and University of Plymouth – is initially focused on the London construction sector. However, we intend to develop and expand the project across the UK in the coming months.
Building a data infrastructure
The Ethos-led partnership was successful in the IUK competition, ‘Solving Urban Challenges Through Data’, and was awarded a grant to conduct a Collaborative Research and Development project, which started formally on 1 October 2015. Further project collaborators providing contribution-in-kind include Crossrail and Greenwich council.
SkillsPlanner aims to help industry, employers, councils, trainers and, ultimately, individual workers to collaborate and share data to enable effective planning for future employment needs. It will be based on a cutting edge Linked and Open Data platform that can aggregate, integrate and analyse skills data from a variety of sources to provide a valuable ’real time’ picture of the skills landscape, mapping industry demand against current training provision.
It is particularly fitting that we are using data to supply construction skills fit for our future homes, buildings and other infrastructure.
Data: an “engine for growth and efficiency”
Our world is increasingly data-driven, and government and industry organisations are beginning to adapt to these changes – if we look again at construction, for example, there has been a strong push to get government projects delivered using data-centric building information modelling processes, mandatory from April 2016.
We are also encouraged by initiatives from the Open Data Institute, with whom we have close links – the ODI chairman and co-founder, Sir Nigel Shadbolt, is talking at our SkillsPlanner launch in London on 24 February, and also chairs Seme4, one of the SkillsPlanner partners. The ODI is urging government to consider data as infrastructure that is fundamental to the operation of a modern society and its economy. With the Royal Statistical Society, the ODI wrote an open letter to the chairman of the new UK Infrastructure Commission saying:
“We are not currently treating data as infrastructure. We are not giving it the same importance as our road, railway and energy networks were given in the industrial revolution and are still given now. We risk seeing data only as a tool for transparency when it should also be an engine of efficiency and growth.”
We like this ambition; it fits with Ethos’s culture and with our ambitions for SkillsPlanner. We want this data platform to harness the power of linked and open data and to be scalable and replicable across many industry sectors – improving the match of skills to jobs, reducing unemployment, increasing local labour supply, and enabling training provision to be responsive to industry needs. If we succeed in this mission, then data will be playing a key role in helping to boost our economy.